

You've heard about the Deployment Management practice part of ITIL4 (Information Technology Infrastructure Library version 4) and you would like to learn more about it?
Previous ITIL versions have placed focus on the processes. In contrast, ITIL 4 emphasizes practices while giving the organization the flexibility to implement specific processes. In this blog post, let's deep dive into the ITIL4 Deployment Management practice and understand what best practices can apply to your own context.
Deployment Management aims to deliver changes to environments in "the BETTER, FASTER, and CHEAPER" way. ITIL 4 Foundation describes the purpose of the Deployment Management practice and its importance between Change and Release Management. 3 practices are linked and necessary to deliver services both fit for use and purpose:
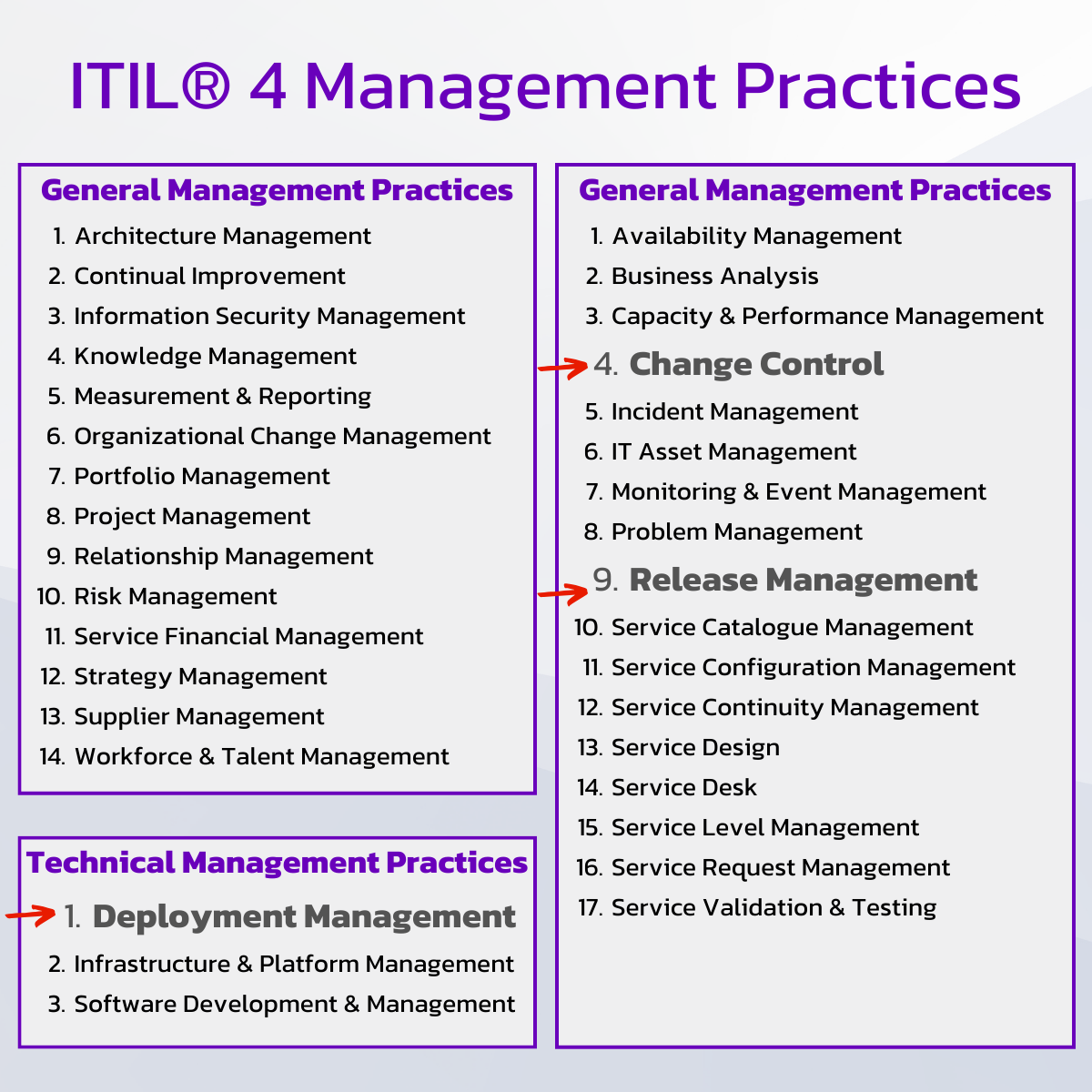
Change Control (sometimes also called "Change Enablement") helps coordinate technical changes to maintain throughput and stability.
Release Management focuses on when and how to make new or updated components available to users.
Deployment Management is the technical vehicle that looks at moving new or changed service components from one environment to another.
Zooming on the Deployment Management practice, there are several deployment techniques available and each company has its own preferences. Depending on their specific services and requirements, some use a combination of these approaches:
Phased delivery focuses on deploying changes gradually across multiple targets.
Continuous delivery leverages DevOps principles, such as rollout in small batch sizes to support Continuous Integration for automated deployments.
Big bang deployment supports the release of features to all targets simultaneously. It's sometimes necessary to mitigate risks by using blue-green deployments that keep two live targets running (old and new) and facilitate traffic to one or the other, making for easier rollback.
Pull deployment allows targets to pull changes "on demand," such as polling a central system for new changes and self-updating as required. This permits the users to control the timing of updates and enables them to request software updates only when needed.
All the above-mentioned deployment techniques can be combined together depending on your needs and can be used for both on-premise and cloud deployments. Also, refer to our article helping you choose between 8 deployment strategies.
Modern application development creates competitive differentiation by enabling rapid innovation. There are some essential guidelines to achieve success when building and deploying:
Focus on decomposing and decoupling apps into micro-services to ease deployment and scale accordingly.
Focus on increasing the checks and feedback through continuous monitoring, also for your non-productive Environments
Make sure you use a proper deployment tool that supports audit and change managementIf your infrastructure or software development is provided as a service, make sure you have access to all information regarding past and future deployments
Ensure security across the whole deployment cycle. You should maintain software components from a central secured repository to avoid changes before deployment.
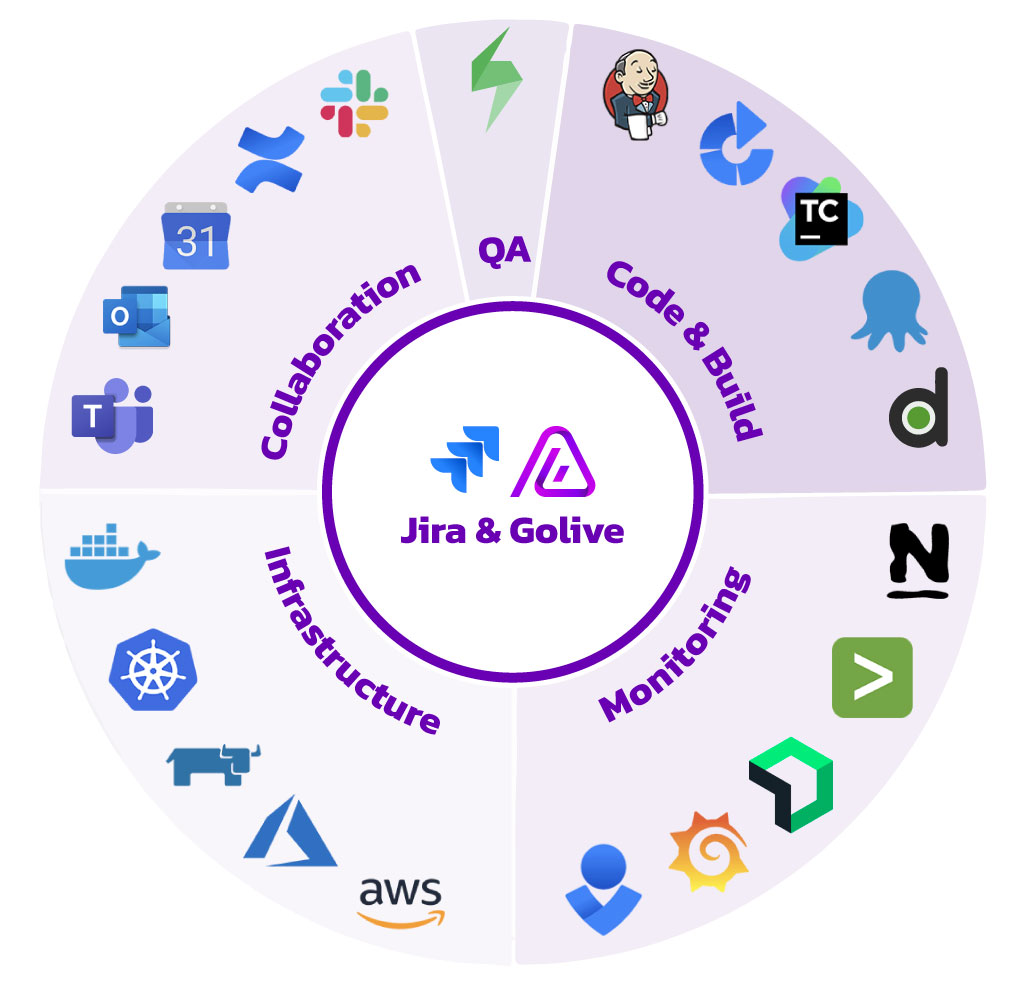
There are plenty of tools available for managing your deployments. To name a few: Jenkins, Octopus Deploy, TeamCity, Bamboo, AWS CodeDeploy, XL Release, Azure DevOps, GitLab CI, etc.
Which key elements should you consider when choosing a deployment tool?
Deployment tools can require very different technical expertise. Make sure to take into consideration your team's expertise and experience when you select a new deployment tool. You want your team to like it so that it can be quickly adopted.
As modern software development projects often use Agile methodologies, there is a strong need to deliver new features frequently.
That's why Continuous Integration (CI) and Continuous Delivery (CD) are key. In order to cut down the time spent on repetitive tasks, you need automation. Look for tools with great automation capabilities.
If you are part of a large organization, you will probably need to support multiple platforms. Make sure your deployment tool is compatible with the main operating systems: Windows, Unix, Linux, Mac OS, Android, and iOS.
Your deployment process should support popular languages like Java, JavaScript, PHP, Python, etc. and it should integrate seamlessly with tools like GitHub.
Because what you need today can be quite different from what you will need in a year, choose a deployment tool that is actively maintained and that can adapt.
It should have a well-documented Rest API and the ability to trigger Webhooks. Integration capabilities leveraging Zapier or similar automation tools will help as well. Many modern tools like Jenkins also offer the possibility to build and install third-party plugins / shared libs.
There is a huge range of deployment management tools available today. While the best ones usually cost money, many are free. And there are lots of free software development tools that have been used to build many great apps!
There are many good reasons for an organization to use multiple deployment tools. And with many tools, it may be complex to get an overview of all cross-application deployments. That's why we have built the Golive for Jira.
It improves communication by connecting to your deployment tools and aggregating useful deployment information in Jira, a tool often used by the whole organization. It displays your cross-platform deployment history, and also helps you schedule your next deployments!
Measuring the effectiveness of your Deployment Management practice ensure continuous improvement and alignment with business objectives. By tracking the right Key Performance Indicators (KPIs) and success metrics, you gain valuable insights into the efficiency and effectiveness of your deployment processes.
Gauging customer satisfaction through surveys and feedback is essential, as happy customers often reflect successful deployments with minimal disruptions. To ensure continued success, it's important to monitor application performance metrics post-deployment, such as response times, error rates, and system resource usage. Stable or improved performance in these areas indicates a successful deployment.
Another critical aspect to track is the user adoption rate, which measures how quickly and extensively new features are adopted by users. High adoption rates typically signify that updates are well-received and valuable. Additionally, monitoring the volume of support tickets related to recent deployments is crucial; a decrease in support tickets can indicate smoother and more reliable deployments.
Lastly, evaluating the cost-efficiency of your deployment process by comparing the resources spent versus the value delivered provides valuable insights. Efficient use of resources often aligns with optimized deployment practices, ensuring that the overall process remains cost-effective and beneficial.
In summary, Deployment Management ITIL 4 bridges the gap between Change Control and Release Management. By adopting the right deployment techniques and tools, you ensure that changes are delivered in a better, faster, and cheaper way. Effective Deployment Management not only enhances service quality but also supports continuous innovation and operational excellence.
By focusing on these key areas, you can optimize your deployment management practice and drive significant improvements in your IT service delivery.